Scars
Burn scars
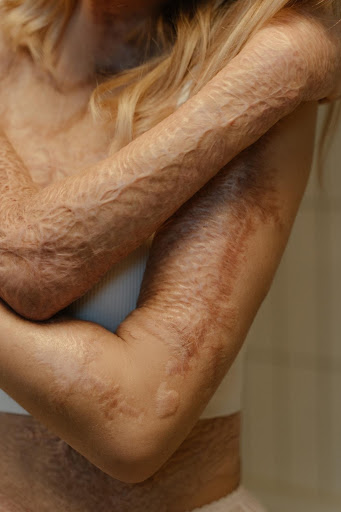
When a burn damages the dermis (known as second- or third-degree burns), we can observe a scar as a sequela. This is especially the case when the skin’s pilosebaceous units, the structures from which the skin regenerates after an aggression, are damaged. The appearance of these scars is variable, although it is common to observe areas of bulging or hypertrophy, alterations in colour (hyper- or hypopigmentation), and changes in texture. They may be associated with itching or pain, and affect the mobility of the area.
Frequently asked questions
Click on the question to expand the answer
The combination of different tools can be the key to improving the appearance of these scars as much as possible. We must take into account the extent, location, whether there is a limitation to movement or tissue alterations (changes in texture or colour).
The most commonly used techniques include the use of lasers such as pulsed dye, non-ablative fractional laser or ablative fractional laser. Other techniques can also be used in the treatment of keloids such as cryotherapy, infiltration of corticosteroids and cytostatics, hydration of the area and the application of silicone gels and patches.
Unlike most scars, which can benefit from early treatment to prevent their progression, in the case of burn scars, 6 months are usually required before starting the most aggressive treatments, as during this time the scar may undergo unpredictable changes that require close monitoring by the doctor (retractions, changes in colouring, pain or itching). After these 6 months, it is recommended not to start treatment more than 18 months after the scar has been produced in order to achieve optimal results.
We can achieve partial or total improvement of the alterations in colouring, redness, itching, pain and stiffness by 50% within 6 months of starting treatment, although this will depend on factors such as the severity of the scars or the patient’s response.
The choice of lasers or light sources will depend on the characteristics of the scar, although in general terms we will use the same as in the case of the treatment of keloids. The most satisfactory responses are achieved through the use or combination of vascular laser, and fractionated ablative and non-ablative fractionated laser.
Although each scar has its own characteristics, in general between 5 and 8 sessions spaced 4 to 6 weeks apart are necessary.
Book an appointment
You can make an appointment by phone, via email, or by filling in this form.
